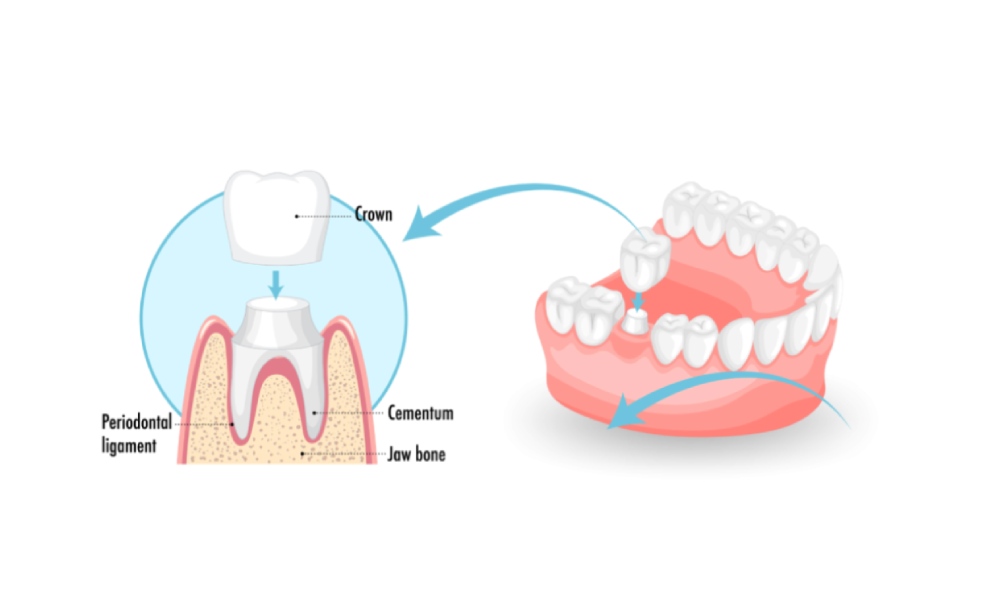
What Are Gum Diseases?
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are infections that damage the gums and surrounding tissues that hold your teeth in place. Left untreated, these conditions can lead to gum recession, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss.
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which causes swollen, red, and bleeding gums, especially while brushing. If not addressed early, it can progress to periodontitis, a more serious infection that affects the bone and connective tissues around the teeth.

Why Gum Health Matters
Did You Know?
More than 50% of Indians experience some form of gum disease — yet with proper oral care and regular dental checkups, most of these issues are entirely preventable!
How to prevent it?
- Brush twice daily and floss regularly
- Visit your dentist every 6 months for professional cleaning
- Eat a balanced, low-sugar diet
- Avoid tobacco and smoking
Types of Gum Disease
Crowns are made using different materials, and each type has its own benefits:
1. Gingivitis
The earliest and most reversible form of gum disease.
Symptoms:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Bad breath
- Sensitivity during brushing or flossing
Causes:
- Plaque buildup
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause)
- Certain medications
- Poor nutrition (especially vitamin C deficiency)
With good oral hygiene and timely dental care, gingivitis is completely treatable.
2. Periodontitiss
An advanced stage of gum disease where the infection spreads beneath the gum line and damages the bone and tissues supporting your teeth.
Symptoms:
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Receding gums
- Painful chewing
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Changes in bite
Stages:
- Mild: Early bone loss and gum pocket formation
- Moderate: Increased tissue damage and bad breath
- Severe: Major bone loss and tooth mobility
If not treated, periodontitis can lead to permanent tooth loss.

Gum Disease: Symptoms to Watch For
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Common warning signs include
- Bleeding gums
- Chronic bad breath
- Loose or mobile teeth
- Gum recession (teeth look longer)
- Pus near gum line
Many of these symptoms can appear without pain, so don’t skip your regular dental exams.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Multiple factors can increase the risk:
Lifestyle Habits
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Poor oral hygiene
- High-stress levels
Health Conditions
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy, menopause)
- Autoimmune disorders
- Low immunity
Dental Problems
- Crooked teeth
- Ill-fitting dental appliances
- Broken fillings
Medications
- Steroids
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Oral contraceptives
- Calcium channel blockers
Diagnosis of Gum Disease
A complete diagnosis includes
1.Medical & Dental History
- Health conditions, lifestyle habits, and symptom review
2.Clinical Examination
- Checking gum color, swelling, and bleeding
- Probing gum pockets to assess disease depth
3.Dental X-Rays
- Evaluating bone loss around teeth
Early diagnosis helps prevent further complications and allows for more conservative treatment.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling & Root Planing)
- Non-surgical procedure to remove plaque and tartar
- Smoothens root surfaces to promote gum healing
- Performed under local anesthesia
2. Antibacterial Therapy
- Prescription mouth rinses or antibiotic gels
- Helps reduce infection and inflammation
3. Surgical Treatments
- Flap surgery: To access deep pockets and clean roots
- Bone grafts: To restore lost bone
- Soft tissue grafts: For receding gums
- Guided tissue regeneration: Encourages tissue growth
4. Laser Therapy
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Targets infected tissues and encourages gum reattachment
- Faster healing and less discomfort
5. Periodontal Maintenance
- Ongoing cleanings every 3–6 months
- Helps keep gum disease under control
Preventing Gum Diseases
Maintaining healthy gums is easier than treating disease. Follow these best practices:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss or use interdental brushes daily
- Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash
- Schedule dental check-ups twice a year
- Avoid tobacco and sugary foods
- Eat a nutrient-rich, balanced diet
Complications of Untreated Gum Disease
Maintaining healthy gums is easier than treating disease. Follow these best practices:
- Tooth Loss – due to loss of bone and gum support
- Jawbone Damage – making future implants difficult
- Gum Recession – exposing roots and causing sensitivity
- Periodontal Abscess – pus formation near infected gums
- Impact on General Health – links to diabetes, heart disease, respiratory problems
- Pregnancy Issues – higher risk of low birth weight or premature delivery
Gum Disease and Whole-Body Health
Gum disease doesn’t only impact your mouth — research links it to several health issues:
- Diabetes –Poor gum health may raise blood sugar levels
- Heart Disease - Gum bacteria may increase heart disease risk
- Respiratory Problems -Inhaled oral bacteria can affect lungs
- Pregnancy Risks - Higher risk of premature birth
- Rheumatoid Arthritis -Inflammation links under study
When Should You Visit a Dentist?
See your dentist if you notice:
- Bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Swollen or receding gums
The earlier gum problems are caught, the simpler and more effective the treatment will be.
Cost of Gum Disease Treatment
The cost of treating gum disease depends on the severity and type of procedure needed — from deep cleanings to surgical interventions. For accurate pricing, we recommend scheduling a consultation at our clinic.
Book Your Gum Health Consultation Today
Your smile starts with healthy gums. Whether you need a deep cleaning or advanced gum care, our experienced dental team is here to help.
Schedule your appointment today and take the first step toward a healthier smile.